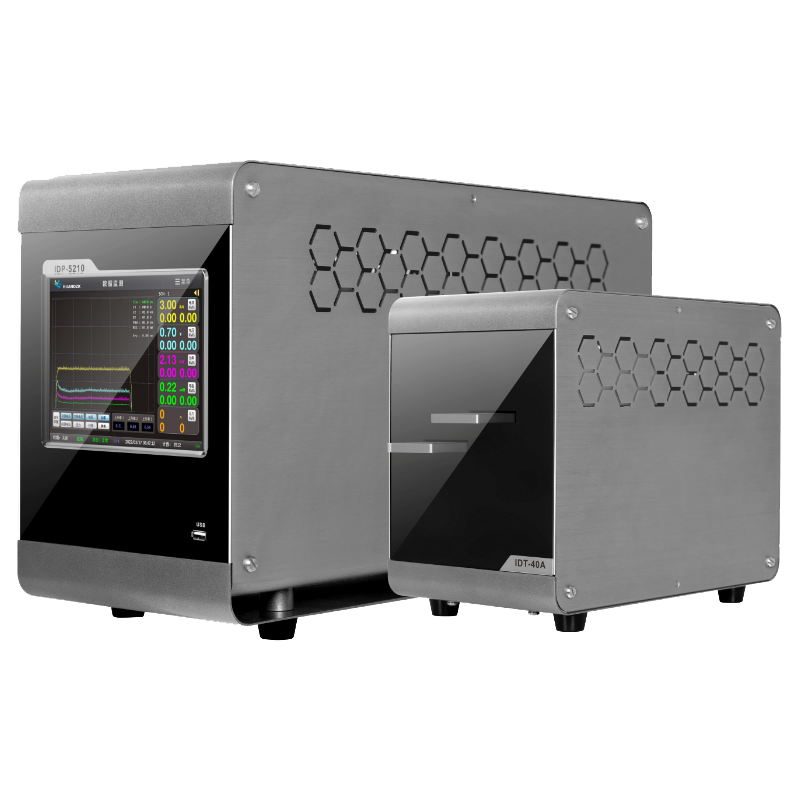
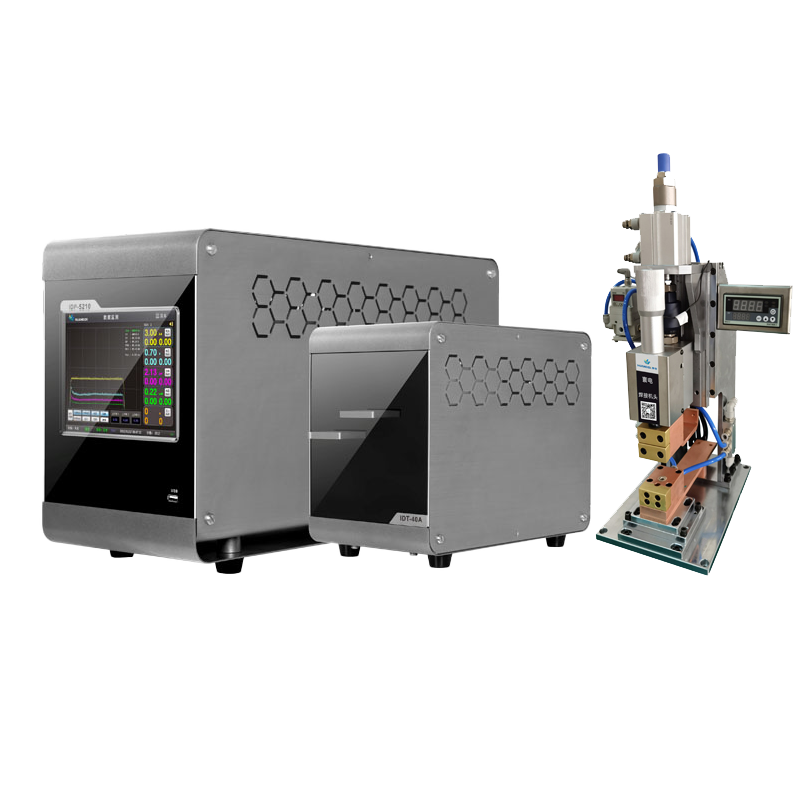
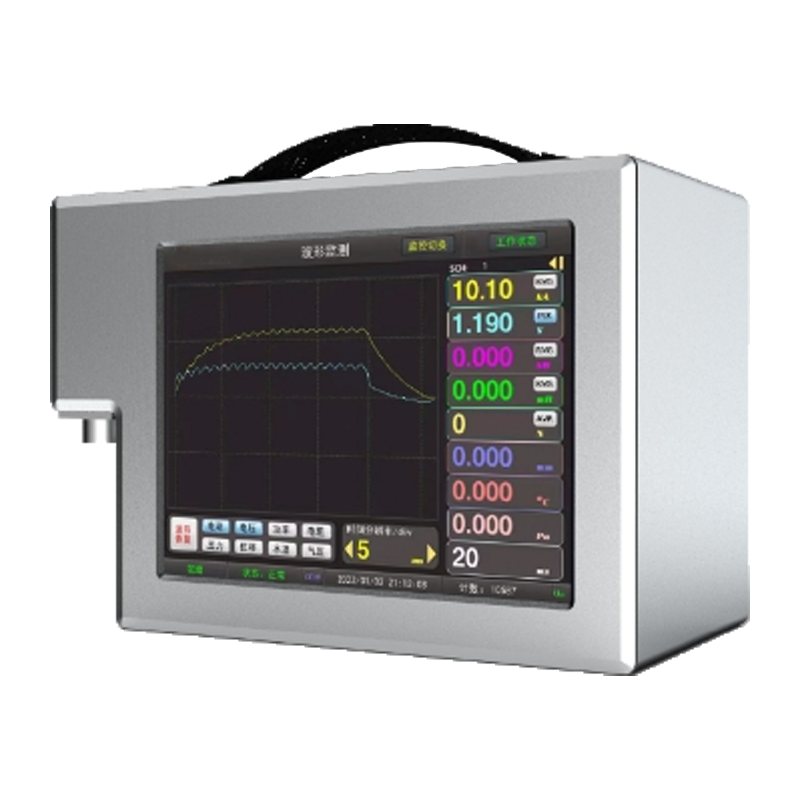
Resistance welding machine, Pulse Thermocompression Welding, Pulse Heat (Hot Bar Reflow) Soldering Machine, Pulse Heat Bonding, and Hot Bar Welding represent five distinct but interrelated technologies widely applied in precision joining processes across electronics, automotive, and medical device manufacturing. Though each operates under different thermal and mechanical principles, they share common objectives: achieving reliable, repeatable, and contamination-free bonds without compromising adjacent materials or components.

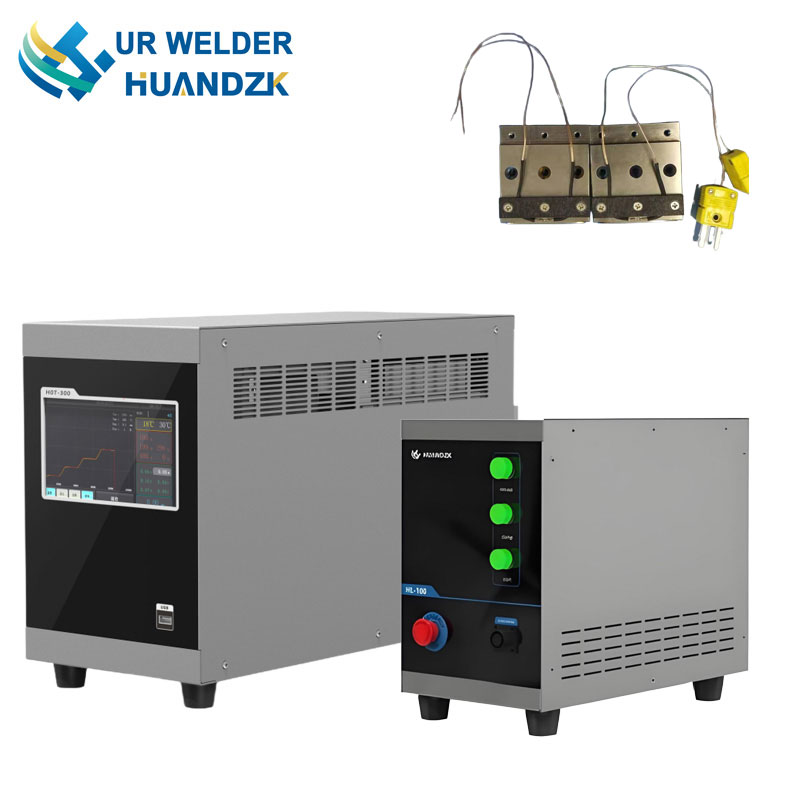
Resistance welding machine utilizes electrical current passed through contacting metal surfaces to generate localized heat via resistance, enabling fusion under applied pressure. Its primary advantage lies in speed and energy efficiency, making it ideal for mass production of battery tabs, wire harnesses, and sheet metal assemblies. Unlike traditional arc or gas welding, Resistance welding machine leaves minimal thermal distortion, preserving structural integrity.
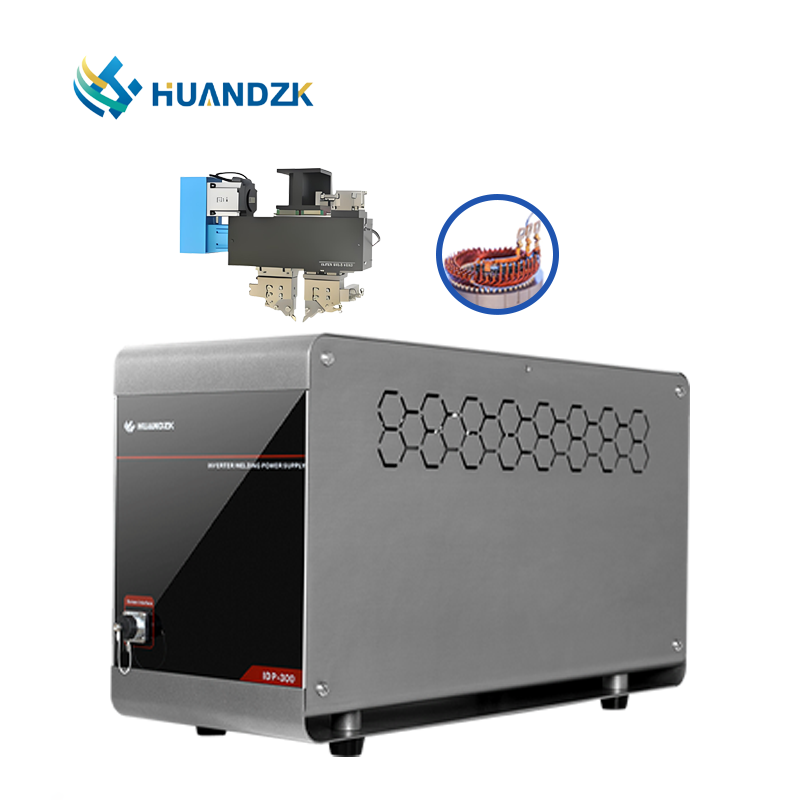
Pulse Thermocompression Welding combines controlled heat and pressure in a single pulse-driven cycle to bond dissimilar or fine-pitch materials — especially gold, aluminum, or copper wires to substrates. This technique is indispensable in semiconductor packaging and microelectronics, where micron-level alignment and minimal intermetallic growth are critical. Pulse Thermocompression Welding ensures consistent interfacial contact while avoiding oxidation, thanks to its inert atmosphere compatibility and millisecond-level pulse control.
Pulse Heat (Hot Bar Reflow) Soldering Machine operates by applying a heated tool — often a thermode — directly onto pre-deposited solder paste or preforms. The pulse-controlled temperature profile melts the solder without overheating surrounding components. This method excels in flexible circuit assembly, LCD/LED display manufacturing, and connector soldering where spatial precision and thermal zoning are non-negotiable. Pulse Heat (Hot Bar Reflow) Soldering Machine allows for programmable ramp-soak-peak profiles, adapting to varying solder alloys and substrate sensitivities.
Pulse Heat Bonding refers to a broader category that includes both conductive adhesive curing and low-temperature metallic bonding using pulsed thermal energy. It is frequently used in touch panel lamination, RFID tag assembly, and flexible printed circuit (FPC) termination. Pulse Heat Bonding systems often integrate real-time temperature feedback and force monitoring to ensure adhesive flow or solder reflow uniformity, minimizing voids and delamination risks.
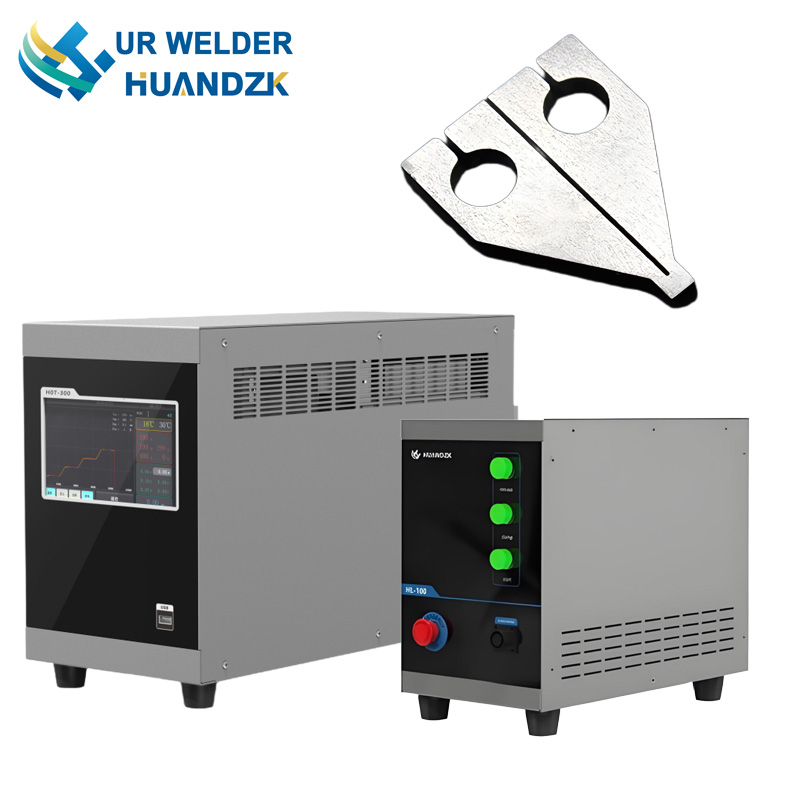
Hot Bar Welding, while sometimes used interchangeably with Pulse Heat Bonding, typically denotes continuous or semi-continuous thermal bonding using a constantly heated bar — though modern implementations increasingly adopt pulsed modes for better control. Hot Bar Welding finds heavy use in sealing thermoplastic films, attaching strain gauges, and assembling membrane switches. Its tooling can be customized with patterns or textures to simultaneously weld and emboss.
Together, Resistance welding machine, Pulse Thermocompression Welding, Pulse Heat (Hot Bar Reflow) Soldering Machine, Pulse Heat Bonding, and Hot Bar Welding form a comprehensive thermal joining toolkit. Their software-driven controls, adaptive profiles, and integration capabilities make them essential in automated production lines, where precision, traceability, and throughput define competitive advantage. Each system, though specialized, contributes to the overarching goal: creating durable, electrically sound, and mechanically stable joints through intelligent thermal management.